Formation of Stationary Waves in an Air Column
Formation of Stationary Waves in an Air Column: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Normal Modes of Oscillation of an Air Column,Fundamental Frequency of Closed Organ Pipe,Harmonics and Overtones in Closed Organ Pipe etc.
Important Questions on Formation of Stationary Waves in an Air Column
The ratio of frequencies of fundamental harmonic produced by an open pipe to that of closed pipe having the same length is:
For a certain organ pipe, the first three resonance frequencies are in the ratio of respectively. If the frequency of fifth harmonic is and the speed of sound in air is the length of the organ pipe is _____ .
An organ pipe long is open at both ends. The speed of sound in air is . The frequency of the second harmonic is _
An open organ pipe of length vibrates in second harmonic mode. The pressure vibration is maximum
Discuss the formation of standing waves in a closed pipe. Show the sixth harmonic of vibration in the closed pipe with a diagram. How many nodes and antinodes are present?
A tuning fork is used to set up a wave in a pipe of length closed at one end (see figure).
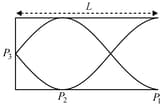
Then,
Why does end correction occur?
What is formula for end correction?
What are limitations of end correction?
What is end correction in physics class 12?
How do you determine end correction?
In stationary waves, antinodes are the points where there is.
In a stationary wave, all particles are
In stationary waves
Mention any four characteristics of a stationary wave.
Pick out the condition which is not required for the formation of stationary waves.
The ratio of first harmonic of open organ pipe and closed organ pipe for the same length is
fundamental frequency of closed organ pipe is ( velocity of sound in air, Length of organ pipe)
Fundamental frequency of open organ pipe is ( Velocity of sound in air, Length of pipe)
End correction is a correction in :
